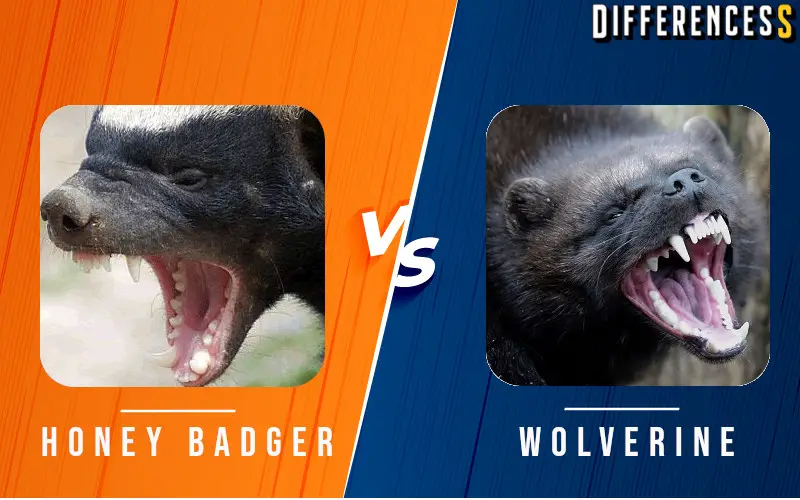
Wolverine and Honey badger both are ferocious animals that are known to drive away animals even bigger than their size. Wolverine and Honey badger belong to the Mustelidae family. But, what would happen if they encounter each other?? Who would win if an animal duel occurs between Wolverine and Honeybadger?? To determine the winner we need to look into their different traits; let’s know about them.
Post Contents
Physical Traits:
Wolverines are the largest member of the Mustelidae family similar to which weasels also belong. Due to their small size, they are often attributed as “small bear” or “skunk bear” or “glutton”. Wolverines are 36-45 cm in height having body length ranging between 65-105 cm and can weigh between 9-330 kg. Wolverines have a furry coat which is usually brown or brownish-black having yellow or golden stripes. They have stocky-built, short but powerful legs, round ears, large heads, and sharp claws. Wolverines can outrun any big animals in snow as they have semi-plantigrade gait/locomotion and wide clawed paws; however, the wolverines are not fast animal; they can run at a maximum speed of 30 km/h.
Honey badgers also belong to the Mustelidae family; they have a stocky body, large skull, muscular neck, small eyes, and shoulder-length of about 25 cm. The skin of the honey badgers is thick, loose which is about 6 mm thick to protect itself from predators’ bite and grasp. Honey badger’s half body is black colored whereas its back is grey or white. Sexual dimorphism is present in honey badgers; females are smaller than males. Honey badgers have an average body length of about 60-70 cm, weighing 8-12 kg. Honey badgers have large clawed forefeet.
Behavioral Traits:
Wolverines are solitary animals, they usually live alone and meet during mating season. They are very territorial and intolerant to intruders of same-sex. Wolverines are nocturnal; they hunt during the nights. Wolverines are unaffected by snow, they don’t go in hibernation like bears and are active year-round. Honey badgers live alone; they are nomadic and solitary. They meet only during mating season, male honey badgers defend their burrows by marking them with their distinct smell.
Diet:
Wolverines are omnivorous; they eat foxes, birds, coyotes, squirrels, rabbits, porcupines, beavers, moose, reindeer, roots, seeds, etc. Honey badgers are omnivorous; they are opportunistic foragers its diet comprises rodents, snakes, eggs, dead carcasses, birds, fruits, berries, roots, etc.
Geographical Distribution:
Wolverines are found in the region of North America and Northern Eurasia. They prefer to live far away from the human settlement in undisturbed habitats. Honey badgers have wide distribution; they are found in sub-Saharan Africa, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Iran, Oman, Syria, Yemen, UAE, Jordan, Israel, India, Nepal, Pakistan, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan.
Habitat:
Wolverines live in grasslands, tundra, alpine forests; during the winter season, they live in dens made of snow or rock crevices or burrows. As mentioned earlier they are mainly found in cold regions. Honey badgers live in varied habitats which include grasslands, woodlands, green forests, arid steppes, deserts, rocky hills, thorn forest, etc. They take shelter in rock crevices, caves, burrows; however, they don’t live in extreme desert conditions or the Mediterranean.
Amazing Fun Facts for kids:
- Wolverines are good climbers and excellent swimmers.
- During the forage, female honey badgers can travel up to 10 km whereas male honey badgers can forage about 25 km.
- Honeybadgers are immune to snake venom.
- Like a skunk, honey badgers also have a gland in their backside which they use to mark their territory and to keep predators away.
- Honey badgers have the “Guinness Book record” for being “world’s most fearless animal”.
- Honey Badgers are voracious eaters; they can eat anything.
Wolverine vs Honey badger Fight: Who would win?
Wolverine and Honey badgers both are ferocious and aggressive animals. Wolverine and Honey badgers both have sharp teeth and long claws which can inflict severe damage. Wolverine has thick fur whereas Honey badger’s skin is rugged, hard, and thick which provides enough protection against any attack of the wolverine. Honey badger has excellent stamina, in a close fight it can confront wolverine with high endurance and can fight for a long time; wolverine might get tired which will provide enough chance for Honey badger to attack wolverine. It all boils down to Honey badger having the upper hand in the fight; however, wolverine would be a tough opponent. Honey badger is the winner of the animal duel Honey badger vs Wolverine.
Comparison Chart: Wolverine vs Honey badger
| Comparison Heads | Wolverine | Honeybadger |
|---|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata | Chordata |
| Class | Mammalia | Mammalia |
| Order | Carnivora | Carnivora |
| Family | Mustelidae | Mustelidae |
| Genus | Gulo | Mellivora |
| Species | G. gulo | M. Capensis |
| Found in | Northern Hemisphere, Europe, USA, Canada, Russia Northern Hemisphere, Europe, USA, Canada, Russia | Sub-Saharan Africa and Some parts of Asia |
| Weight | Around 300 lbs | 17-27 lbs |
| Body Length | 65-107 cm | 55-77 cm |
| Lifespan | 5-13 years | 24 years |
Comparison Video: Wolverine vs Honey badger
FAQ’S: Frequently Asked Questions
What animal can kill a wolverine?
bears, wolves and some big carnivores are seen to kill wolverine.
Which snake can kill a honey badger?
Puff Adder
A honey badger has been documented being bitten and killed by a venomous puff adder .
What smells do Badgers hate?
Citronella, Scotch bonnet peppers and Olbas oil can deter the badgers as they hate their smell
Do Honey Badgers make good pets? can we tame them
Certainly not, They are not social animals, do not like to be held,cuddles and are not playful.
What is a Badgers Favourite food?
Earthworms constitutes up around 80% of their diet.
Badgers are known to eat small mammals like frogs, toads,mice, rats, rabbits, and hedgehogs.