When it comes to heart medications, there are three types that are the most commonly prescribed – inotropic, chronotropic, and dromotropic. And while these terms might sound complicated, they’re actually pretty simple. In this article, we’ll explore what each term means and what effects they have on the heart.
Post Contents
- What is an Inotropic?
- What is an Atropine?
- What is a chronotropic?
- What is a dromotropic?
- How do Dromotropic Agents work?
- How do Inotropes work?
- How do Chronotropes work?
- What are the benefits of each type of medication?
- How These Agents Work
- Examples of Common Drugs
- Benefits of Each Type
- Summary Table
- Conclusion
What is an Inotropic?
Inotropic drugs are those that increase the heart rate. They are used to treat a variety of medical conditions, including high blood pressure, congestive heart failure, and arrhythmias. These drugs can be classified according to their mechanism of action: chronotropic (those that increase heart rate due to a change in the speed of the heart), dromotropic (those that increase heart rate through activation of the vagus nerve), or prostaglandin analogues (such as indomethacin).
What is an Atropine?
An atropine is a type of drug that dilates blood vessels. This can make it easier for the body to get oxygen and other nutrients. It is sometimes used to treat heart failure, high blood pressure, and other conditions.
What is a chronotropic?
Dromotropic is a type of medication that slows the heart rate. It is most commonly used to treat low blood pressure and heart failure. In contrast, an inotropic agent speeds up the heart rate. This can be used to treat a wide range of medical conditions, including cardiac arrest and high blood pressure.
What is a dromotropic?
Dromotropic drugs are designed to affect the muscles in different ways. They can cause an increase in heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration. This is often used to treat conditions like anxiety or a lack of energy.
How do Dromotropic Agents work?
Dromotropic agents are drugs that work by increasing or decreasing the heart rate. They are often used to treat things like anxiety, stress, and cardiac arrhythmias. The most common dromotropic agents are epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine.
Chronotropic agents work to slow the heart rate down. They are often used to treat things like heart failure and coronary artery disease. The most common chronotropic agents are atropine (hyoscine) and bradykinin.
How do Inotropes work?
Inotropes are medications that work by increasing the activity of the sympathetic nervous system. This increases blood flow and oxygen delivery to the body’s tissue, which can lead to increased energy and performance. Inotropes are most commonly used in the treatment of heart disease and high blood pressure, but they are also used to treat a variety of other conditions.
Chronotropes work by increasing the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system. This decreases blood flow and oxygen delivery to the body’s tissue, which can lead to decreased energy and performance. Chronotropes are most commonly used in the treatment of stress and asthma, but they are also used to treat a variety of other conditions.
Dromotropic drugs act on both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The two systems work together to control different parts of the body, so dromotropic drugs have a dual effect on how they work. Dromotropic drugs are most commonly used in the treatment of stroke, heart failure, and seizure disorders.
How do Chronotropes work?
Chronotropes are a type of drug that work by increasing the heart rate. This can be helpful in treating conditions such as cardiac arrest or high blood pressure. They work by boosting the body’s natural pacemaker, known as the sympathetic nervous system.
Dromotropes are a type of drug that work by decreasing the heart rate. This can be helpful in treating conditions such as cardiac arrest or high blood pressure. They work by slowing down the body’s natural pacemaker, known as the parasympathetic nervous system.
What are the benefits of each type of medication?
Inotropic medications are used to increase the activity of the heart. These medications work by increasing the amount of blood flowing through the heart. Chronotropic medications work by slowing down the heart rate. Dromotropic medications work by enhancing blood flow in certain areas of the body. All three types of medications can have a variety of benefits, depending on the individual patient.
Some common benefits of inotropic medications include improved cardiac function, reduced symptoms and improved breathing. Some common benefits of chronotropic medications include decreased anxiety, improved sleep and relief from angina pain. Dromotropic medications may also help improve circulation and relieve pain in areas such as the feet and hands.
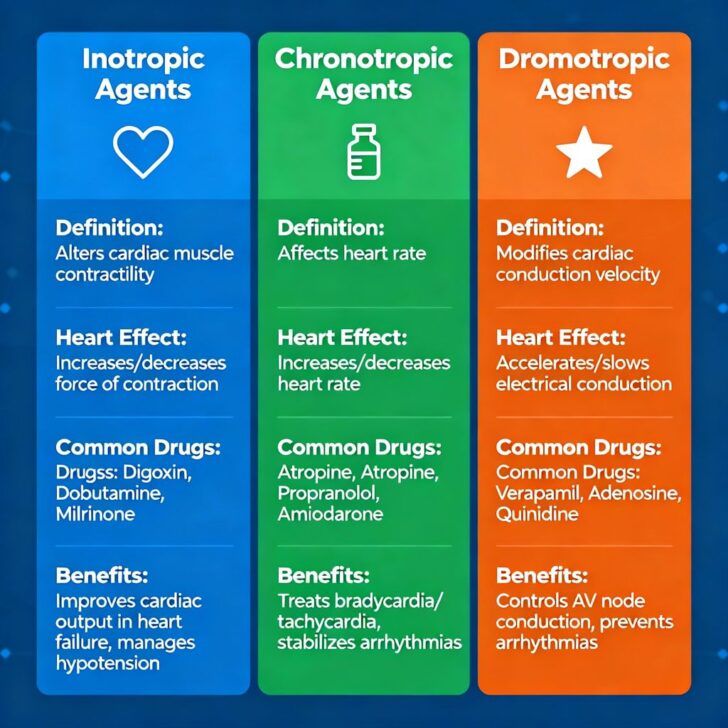
How These Agents Work
-
Inotropic Drugs: Increase the strength of heart contractions by altering calcium availability in cardiac muscle cells, thus augmenting cardiac output.
-
Chronotropic Drugs: Modify the heart rate by acting on the sinoatrial node (the heart’s natural pacemaker), either increasing or decreasing its pacing.
-
Dromotropic Drugs: Affect the speed of electrical impulses in the conduction pathways, helping stabilize rhythm disturbances.
Examples of Common Drugs
-
Inotropic: Digoxin (positive inotrope used in heart failure), Beta-agonists like dopamine.
-
Chronotropic: Atropine (positive chronotrope used to increase heart rate), Beta-blockers (negative chronotropes).
-
Dromotropic: Calcium channel blockers (negative dromotropes), Epinephrine (positive dromotrope).
Benefits of Each Type
-
Inotropic Agents: Improve cardiac output, help in treating heart failure, and improve symptoms like breathlessness and fatigue.
-
Chronotropic Agents: Manage heart rate abnormalities, improving circulation and reducing symptoms caused by abnormal rates.
-
Dromotropic Agents: Control conduction abnormalities in the heart, help manage arrhythmias and improve coordinated heartbeats.
Summary Table
| Agent Type | Primary Effect | Target Area | Common Drugs | Main Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inotropic | Increases/Decreases contraction force | Cardiac muscle | Digoxin, Dopamine | Improves cardiac output |
| Chronotropic | Increases/Decreases heart rate | Sinoatrial node | Atropine, Beta-blockers | Controls arrhythmias and rate issues |
| Dromotropic | Increases/Decreases conduction velocity | Atrioventricular node | Calcium channel blockers, Epinephrine | Manages heart blocks and arrhythmias |
Conclusion
Inotropes, chronotropes, and dromotropes are all types of drugs that work to increase the heart’s ability to pump blood. However, they differ in how they do this and what effects they have on the body. Inotropic drugs help to improve the overall force of contraction by increasing the amount of calcium that is available to contract muscle cells. Chronotropic drugs work by slowing down the heart rate, and dromotropic drugs help to slow down or stop the movement of blood through the vessels of the heart.